





Професор має 10 наукових публікацій з радіології та онкології в медичних журналах.
Член таких організацій, як:
Спеціалізується на лікуванні злоякісних новоутворень за допомогою радіотерапії та комбінованих методів. Здійснює діагностику захворювання з використанням передового обладнання та сучасних аналізів. Після отримання даних про розміри, розташування та форму пухлини, лікар визначає оптимальну дозу випромінювання і вибирає найкращий метод доставки випромінювання до пухлини.
Лікар ретельно моніторить стан пацієнта протягом усього лікування, контролює зміни у клітинах новоутворення. При необхідності адаптує курс лікування, вирішуючи, чи варто внести більш інтенсивний або м’якіший план боротьби з пухлиною і метастазами. Має високий рівень позитивної статистики виживання серед пацієнтів.
Має багато публікацій у зарубіжних наукових журналах (на основі Національної Медичної Бібліотеки США (National Library of Medicine, NLM))











Дізнайтесь вартість лікування та отримайте компенсацію на лікування до 20 000 €
Допоможемо в оплаті лікування дітей до 20 000 €
Медичний консультант
Медичний консультант
Німецький онколог-імунолог складе індивідуальну програму імунотерапії.
Іспанський онколог-імунолог складе індивідуальну програму імунотерапії.
Турецький онколог-імунолог складе індивідуальну програму імунотерапії.
Турецький променевий терапевт підготує індивідуальну програму променевої терапії
Ізраїльський променевий терапевт складе індивідуальну програму променевої терапії.
Німецький променевий терапевт складе індивідуальну програму променевої терапії.
Іспанський променевий терапевт складе індивідуальну програму променевої терапії.
Турецький пластичний хірург складе індивідуальну програму операції.
Німецький пластичний хірург складе індивідуальну програму операції.
Іспанський пластичний хірург складе індивідуальну програму операції.
Ізраїльський пластичний хірург складе індивідуальну програму операції.
Турецький хірург-ортопед складе індивідуальну програму операції.
Ізраїльський хірург-ортопед складе індивідуальну програму операції.
Німецький хірург-ортопед складе індивідуальну програму операції.
Італійський хірург-ортопед складе індивідуальну програму операції.
Литовський хірург-ортопед складе індивідуальну програму операції.
Польський хірург-ортопед складе індивідуальну програму операції.
Український хірург-ортопед складатиме індивідуальну програму операції.
Іспанський хірург-ортопед складе індивідуальну програму операції.
Турецький нейрохірург вивчить медичну ситуацію і дасть рекомендації щодо лікування.
Іспанський нейрохірург вивчить медичну ситуацію і дасть рекомендації щодо лікування.
Ізраїльський нейрохірург вивчить медичну ситуацію і дасть рекомендації щодо лікування.
Турецкий нейрохірург вивчить медичну ситуацію і дасть рекомендації щодо лікування.
Німецький нейрохірург вивчить медичну ситуацію і дасть рекомендації щодо лікування.
Турецький хірург вивчить медичну ситуацію та дасть рекомендації щодо лікування.
Німецкий хірург вивчить медичну ситуацію та дасть рекомендації щодо лікування.
Іспанський хірург вивчить медичну ситуацію та дасть рекомендації щодо лікування.
Ізраїльский хірург вивчить медичну ситуацію та дасть рекомендації щодо лікування.
Німецький лікар детально вивчить вашу ситуацію та відповість на всі запитання
Турецький лікар детально вивчить вашу ситуацію та відповість на всі запитання
Ізраїльский лікар детально вивчить вашу ситуацію та відповість на всі запитання
Вивчивши вашу ситуацію, лікар складе індивідуальну цінову пропозицію.
Лікар-консультант відповість на всі ваші запитання щодо вартості лікування, вибору лікаря та повністю організує лікування за кордоном.

ми зв'яжемося з вами протягом 15 хвилин

Обидва методи передбачають проведення дистанційного опромінення проблемної галузі. Відмінності стосуються інтенсивності дії. Променева терапія проводиться курсом із кількох сеансів, які виконуються з певною кратністю. Тривалість курсу становить від 1 до 7 тижнів. Метод радіохірургії передбачає швидке знищення пухлини за сеанс.
В обох випадках для опромінення використовують спеціалізовані установки – лінійні прискорювачі. Для потреб радіохірургії лінійні прискорювачі мають вбудовані коліматори, що дозволяють опромінювати невеликі мішені складної форми, у тому числі ті, які розташовані поряд із радіочутливими внутрішньочерепними структурами.
Основним критерієм вибору найбільш відповідної інтенсивності впливу є розмір ракового вузла. За допомогою методу радіохірургії можна заодно видалити відносно невеликі пухлини. Обмеження за розміром вводиться у зв’язку з тим, що руйнування тканин супроводжується виходом у кров та лімфу токсинів, що утилізуються за участю нирок та печінки. Об’ємні злоякісні новоутворення краще видаляти за кілька сеансів. Це дає можливість організму справлятися з інтоксикацією, не перевантажуючи життєво важливі органи.
Кожен вид променевої терапії має ряд особливостей, які визначають коло показань і протипоказань до їх застосування в онкології. Наприклад, для лікування злоякісних новоутворень найчастіше використовують гамма-терапію та рентгенівське опромінення завдяки їх здатності проникати в тканини на задану глибину і надавати передбачувану дозозалежну дію на пухлину.
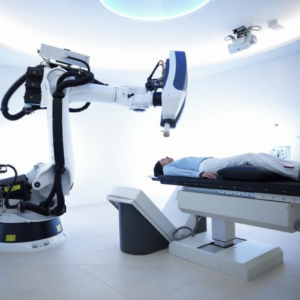 Гамма-ніж
Гамма-ніжОдним із напрямків гамма-терапії є гамма-ніж. Метод передбачає використання джерел гамма-випромінювання високої інтенсивності, здатних створювати значні дози радіації в глибоко розташованих пухлинах і тим самим знищувати весь раковий вузол.Використовується гама-ніж тільки для видалення доброякісних і злоякісних пухлин у головному мозку. Крім того, його застосовують для лікування судинних захворювань (артеріовенозних мальформацій) і функціональних хвороб – невралгії трійчастого нерва, паркінсонізму, епілепсії.
CyberKnife — радіохірургічна система, яка використовує рентгенівське та гамма-випромінювання. Система в режимі реального часу відстежує локалізацію пухлини, яка зміщується під час дихання або скорочення м’язів. Прикладом можуть служити пухлини легенів, кишечника, простати. Це підвищує точність впливу на ракову пухлину і сприяє збереженню життєздатності навколишніх здорових тканин. Розмір і глибина пухлини не є обмеженням для використання Кіберножа.
Лінійний прискорювач TrueBeam вивів променеву терапію на новий рівень. Пристрій поєднує в собі переваги всіх сучасних лінійних прискорювачів і значно перевершує їх за характеристиками та можливостями:
надточне фокусування та налаштування променя, що дозволяє впливати тільки на тіло пухлини (точність налаштування 0,05 мм);
скорочення кількості сеансів для повного знищення пухлини (3-5 сеансів замість 20-35 сеансів);
скорочення часу одного сеансу до 5-20 хвилин;
покращений візуальний контроль та можливість коригувати положення пацієнта без переривання процедури;
автоматичне налаштування променя з поправкою на рухи тіла під час вдиху та видиху;
зменшення та повне виключення опромінення здорових тканин.
Людський фактор при проведенні променевої терапії із застосуванням лінійного прискорювача Трубім зведений до мінімуму: комп’ютер самостійно аналізує отримані під час діагностики дані та налаштовує випромінювачі відповідно до них. У ході процедури установка контролює точність та потужність випромінювання з інтервалом у кілька мілісекунд. Це дозволяє провести опромінення чи видалення пухлини з мінімальними наслідками для організму.
Вплив нейтронним випромінюванням ефективний у пацієнтів з радіорезистентними пухлинами, стійкими до іонізуючого випромінювання. Деякі форми раку мозку, пухлини слинних залоз, саркоми м’яких тканин і більшість рецидивуючих і метастатичних злоякісних новоутворень часто радіорезистентні.
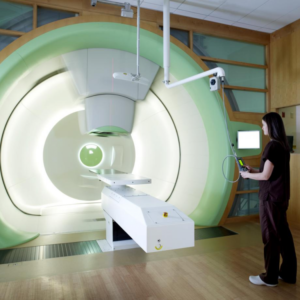 Протонна терапія
Протонна терапіяВикористання розігнаних до високих енергій протонів у синхрофазотронах для лікування онкологічних захворювань є перспективним напрямком медицини. При цьому методі лікування:
Протонотерапія призначається для лікування всіх видів доброякісних і злоякісних новоутворень. Але в першу чергу використання методу доцільно при виявленні радіорезистентних пухлин і, при необхідності, повторному курсі променевої терапії, коли пацієнт вже отримав максимально можливу дозу опромінення, але повне видалення пухлини встигає. не досягнуто. пухлина.
Не секрет, що поява списаного за кордоном медичного обладнання є справжнім технологічним проривом для лікарні. Однак результати лікування таким обладнанням не завжди виправдовують очікування онкохворих.
Experts Medical рекомендують розглядати для лікування медичні центри Туреччини. Наприклад, клініку Емсей в Стамбулі. Вартість променевої терапії в Туреччині приблизно така ж, як і в країнах СНД. При цьому турецькі клініки кожні 5 років оновлюють обладнання, а різноманітність складних апаратів для променевої терапії та радіохірургії дозволяє точно підібрати апарат для конкретного типу пухлини.