Skin cancer treatment abroad

- Below you will find a ranking of the best clinics and doctors specializing in skin cancer treatment abroad.
- The clinics are selected based on the effectiveness of treatment, the qualifications of doctors, the ratio of price and quality, the level of service, and the equipment producibility.
- We personally checked these clinics and can recommend them to our patients.


You don't pay for the services of Experts Medical
as we are representatives of more than 100 foreign clinics

You get treatment without extra fees
You make all payments only at the clinic upon arrival
The best oncologists for skin cancer treatment abroad
Specialization: lung cancer.
Education:
- Higher medical education, graduated from the medical faculty of the University of Padua, Italy;
- Internship in the field of general oncology at the Tel Hashomer Medical Center, Israel;
- Internship in Oncology and Radiation Therapy of the Lungs in Paris, France.
Clinical and scientific experience:
- Participant in numerous clinical trials to combat advanced non-small cell lung cancer;
- Associate Professor at the Faculty of Medicine. Sackler, Tel Aviv University;
- Participant and speaker of Israeli and international conferences;
- Author of scientific articles and publications in the field of non-small cell lung cancer.
Membership in associations:
- International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC);
- American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO);
- European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO);
- European Association for Research on Cancer (EACR);
- Israeli Society of Clinical Oncologists and Radiation Therapists.
The professor runs the Shaare Zedek Cancer Center.
Specialization:
- pulmonology;
- thoracic oncology;
- immuno-oncology;
- immunotherapy.
He takes part in scientific and clinical research of one of the most dangerous types of oncology – lung cancer.
Author of more than 100 scientific papers on methods of early detection of lung cancer and immuno-oncology.
Membership in professional associations:
- Assembly of Thoracic Oncology, Chairman;
- American Society of Clinical Oncology;
- Israeli Association of Pulmonologists;
- Israeli Society for Clinical Oncology;
- European Respiratory Association;
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine;
- World Association for Lung Cancer Therapy.
Dr. Bulent Karagoz is a highly qualified Turkish oncologist, sarcoma and lymphoma specialist, and breast cancer surgeon.
Professor at the Faculty of Medicine at Istanbul Okan University, he served as head of the Department of Internal Medicine.
Author of over 40 publications on cancer research. His research interests are focused on the biology of tumors, as well as the use of immunotherapy in the fight against cancer.
Since 2019, he has been accepting patients at the Anadolu clinic.
Education:
- 1992 – Military Medical Academy. Gulhane, degree in general medicine;
- 1999 – GATA Teaching Hospital Haydarpasa, specialty in internal medicine;
- 2006 – GATA Teaching Hospital Haydarpasa, specialty in medical oncology.
Membership in associations:
- Turkish Medical Oncology Association.
The main specialization is surgical treatment of skin diseases (skin cancer, lymphoma, psoriasis, melonoma, etc.), biological therapy and extracorporeal photophoresis.
Education and professional activity:
- 1990-1997 – Faculty of Medicine, Free University of Berlin, Germany;
- 1993 Clinical Fellowship, John Radcliffe Hospital, University of Oxford, UK;
- 1997-1999 – Assistant Physician, Department of Pathology, Medical School. Benjamin Franklin, Free University of Berlin;
- 1999-2003 – Assistant Physician, Department of Dermatovenereology, Benjamin Franklin Medical School, Free University of Berlin;
- 2003-2004 – Specialist Physician, Department of Dermatovenereology, Benjamin Franklin Medical School, Free University of Berlin;
- 2005-2008 – Senior Physician, Department of Dermatology, Charité University Medical Complex;
- 2004-2008 – Head of the Lymphoma Section at the Charité Skin Cancer Center;
- since 2009 – director of the clinic for dermatovenereology Helios Krefeld, academic hospital of the University. Heinrich Hein, Düsseldorf.
Grants:
- Research grant in Histopathology (German Society for Dermatology);
- Research grant from the Berlin Foundation for Dermatology (for outstanding research in the pathogenesis and diagnosis of cutaneous lymphomas).
Author of more than 167 scientific publications. Regularly takes part in international and national scientific and practical congresses and conferences.
Membership:
- German Society of Dermatovenerologists.
Best clinics for skin cancer treatment abroad







we will contact you within 15 minutes
Programs for skin cancer treatment abroad
Chemotherapy for skin cancer
- Hospitalization: 3 days
- Duration of stay abroad: depending on the chemo protocol, multiple courses of chemotherapy may be required
- Day 1: Meeting at the airport, examination, consultation
- Day 3: Discharge from the hospital and accommodation in a hotel
- Day 5: Control examination
- Day 6: Transfer to the airport
Surgery to remove skin cancer
- Hospitalization: 1 day
- Duration of stay abroad: 6 days
- 1 day: Meeting at the airport, examination, consultation
- 2 day: Surgery, hospitalization
- 3 day: Discharge from the hospital and accommodation in a hotel
- 5 day: Control consultation
- 6 day: Transfer to the airport
Radiation therapy in the treatment of skin cancer
- Hospitalization: Outpatient
- Duration of stay abroad: 11-30 days
- 1 day: Meeting at the airport, examination, consultation
- days 2-10/29: Irradiation, daily (except weekends)
- 11-30 day: Transfer to the airport
Skin cancer treatment abroad involves a personalized approach to patients depending on the type of disease. After a thorough diagnosis, foreign doctors individually select a treatment protocol and type of surgical intervention.
There are 4 main forms of skin cancer according to medical classification. Each of them has its own specific characteristics:
- Basal cell skin cancer is characterized by fairly rare metastasis and, at first glance, does not pose much danger, but this is not always the case. If left untreated, it can cause serious damage to the skin. In the worst case, basal cell carcinoma leads to the destruction of cartilage and bone tissue.
- Squamous cell skin cancer is the most malignant epithelial tumor. It accounts for about 20% of all types of skin cancer.
- Adenocarcinoma is a tumor that originates from glandular epithelial cells. This disease is characterized by rapid penetration into other tissues of the body.
- Melanoma is a malignant tumor originating from pigment cells—melanocytes. The oncological process quickly spreads to organs close to the lesion.
According to the Association of the American Academy of Dermatology, malignancy can occur on any part of the skin, from the scalp to the soles of the feet. Skin cancer can start under a fingernail, on the genitals, in the mouth, or on the lip.
Anyone can suspect that they have a tumor if they pay attention to:
- the appearance of new moles;
- strange shape of papilloma and warts;
- dark spots on the skin.
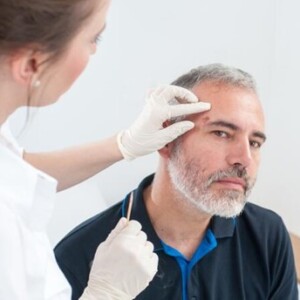
To make an accurate diagnosis, doctors at foreign clinics always perform a biopsy on a suspicious skin area for patients.
Skin biopsy is the most reliable diagnostic method for oncology. Thanks to this study, the doctor can understand what type of skin cancer the patient has. This approach allows foreign oncologists to achieve good treatment results.
In addition to tumor biopsy, patients undergo CT and MRI diagnostics using the latest-generation devices. This allows us to identify possible metastases in other organs.
Oncology check-ups are available in foreign clinics – comprehensive examinations to detect pathology. It can be taken by patients who have a family history of skin cancer or who are suspected of having the disease at the moment.
Patients need to know.
To make an accurate diagnosis, doctors in foreign clinics perform dermatoscopy – an examination of all suspicious formations on the skin with a particular device. A digital dermatoscope allows us not only to examine all skin layers but also to take digital photographs of these structures and analyze them on a computer monitor. With the help of dermatoscopy, doctors establish a preliminary diagnosis of skin cancer.
The next stage of diagnosis is a biopsy with histology. Thanks to this study, they determine what type of skin cancer the patient has and its stage. In some types of this cancer, patients undergo MRI to detect possible metastases in other organs.
In foreign clinics, there are available oncological check-ups – complex examinations for early detection of different types of cancer, including malignant skin tumors, with the help of dermatoscopy. Such check-ups are available to patients who have a family history of skin cancer or have an assumption of the current presence of the disease.
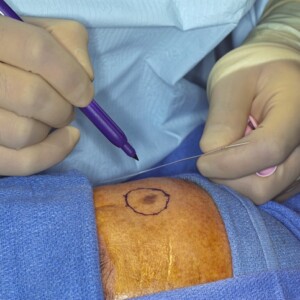
Depending on the specific situation, doctors choose the most appropriate biopsy method. Research options may be:
- Incisional biopsy. The doctor uses a surgical knife to remove a small piece of the abnormal area. He then sutures the area. The sutures last about a week and often do not require removal in a hospital setting.
Excisional biopsy. The doctor uses the same instruments as for an incisional biopsy. But at the same time, it removes the border of healthy tissue around the abnormal area. After the procedure, stitches may also be required. - Needle biopsy. The doctor uses a special instrument to remove a sample of tissue. Remove a small circle covering the entire thickness of the skin. The patient may need stitches to close the area.
- Shave biopsy. The specialist uses a tool to shave off the top layer of skin. Typically, doctors use a device to seal the blood vessels to prevent bleeding. The wound forms a scab and heals without stitches.
Modern treatment of melanoma abroad includes a wide range of operations and drug and device therapy. Surgery for melanoma may involve excision of the abnormal area, sentinel lymph node biopsy (sentinel biopsy), and lymph node dissection (removal of affected lymph nodes).
Non-surgical treatments may include immunotherapy, targeted therapy, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and palliative care. Immunotherapy is used to boost the patient’s immune system, while targeted therapy is used in cases of advanced disease.
The choice of melanoma treatment methods abroad depends on the following factors:
- depth of tumor invasion;
- location of the tumor;
- presence of secondary foci;
- the patient’s age and general condition of the body.
Treatment of skin cancer abroad involves using the most effective protocols by doctors. Often, the treatment regimen is supplemented with medications that are not available to patients at their place of residence. Therefore, people from Asian and Eastern European countries often choose Turkish, Israeli, and German clinics.
TIL (tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes) are tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes that are a component of a malignant neoplasm. Their role in tumor growth and progression has been debated for decades. In modern medicine, the emphasis has shifted to the beneficial effects of TILs on the patient. Methods for treating melanoma have appeared abroad, which make it possible to suppress immunity in the tumor microenvironment.
According to the Israeli Sourasky Clinic, using the TIL protocol in treating melanoma at stage 4 gives results of up to 100%.
How is TIL cell therapy used? The oncologist removes the tumor element and sends it to the laboratory. There, lymphocytes are isolated from tumor tissue and artificially multiplied. After about 3 weeks, these blood cells are injected into the patient, and they begin to fight the melanoma.
Effective treatment of skin cancer abroad is often carried out using targeted therapy. To do this, doctors use drugs that detect and stop the actions of molecules that provoke the growth of cancer cells. Targeted therapy “targets” changes in abnormal cells and does not affect healthy tissue in the body.
What are C-KIT inhibitors? Mutations in KIT are most commonly observed in certain subtypes of melanoma. Common in acral lentiginous melanoma (palms, soles, and nail beds), mucosal melanomas, and melanomas associated with extensive sun damage. Clinical trials have demonstrated tumor reduction with KIT inhibitors.
Foreign oncology clinics are currently testing KIT inhibitors alone or in combination with immunotherapy. In some cases, patients may also be prescribed combination targeted chemotherapy.
Chemotherapy drugs are used to destroy abnormal cells. For cancer limited to the top layer of skin, creams or lotions containing anticancer agents can be applied superficially.
Systemic chemotherapy is used as the main treatment for skin cancer abroad in cases where the disease has spread to other structures of the body. At the same time, patients in foreign hospitals have access to the safest chemotherapy drugs that do not cause severe side effects.
Biotherapy uses the body’s immune system to destroy cancer cells. This type of treatment is one of the most progressive and effective.
Virotherapy is one of the scientifically proven methods of biological cancer therapy. The Latvian medical center Pallas Clinic has laboratories where they create individual medications for each patient.
How does this happen? Lymphocytes and monocytes are collected from the patient and then processed in the laboratory. From them, a clone of immune cells is grown, which can destroy cancer. The medicine is administered intramuscularly as a vaccine.
Virotherapy, in combination with chemotherapy, increases the life expectancy of a person with melanoma.
Radiation therapy uses powerful energy beams, such as X-rays, to kill cancer cells. Modern radiation therapy may be a good option when the tumor cannot be completely removed during surgery.
Doctors provide radiation therapy to patients using the latest-generation installations in the world’s leading clinics. This allows you to achieve the desired result in fewer sessions and without damaging the body’s healthy tissues.
This procedure destroys skin cancer cells using a combination of laser light and a light-sensitive drug.
Foreign doctors have achieved particular success in treating squamous cell skin cancer using photodynamic therapy. PDT is also used to treat pretumor and superficial forms of skin cancer (actinic keratoses, basal cell carcinoma, and Bowen’s disease).
According to research at Johns Hopkins University, surgery is a common treatment for skin cancer overseas. It is used in leading medical centers, taking into account the characteristics of the disease.
Cryosurgery
The surgery involves the process of spraying liquid nitrogen onto the skin to freeze and destroy abnormal tissue.
This method can be used for malignant and benign skin lesions. The procedure is usually used in cases of precancerous lesions or skin cancer isolated to a small area.
Cryosurgery is less traumatic than treating skin cancer abroad using other surgical methods. The patient requires a short recovery time.
Curettage and electrosurgery
Curettage is the process of scraping away cancerous skin tissue. Electrosurgery (burning tissue with an electric current) is used after curettage to stop bleeding and kill the remaining cancer cells. This comprehensive procedure is successful for small and well-defined skin tumors.
Mohs surgery is a technique named after its inventor, Dr. Frederick Mohs, MD. Doctors use this technique to treat various types of skin cancer, including those located in the head and neck area.
The procedure is unique because a microscopic examination of the cancerous tissue is performed during the operation, not after it.
The MOHS method is more time-consuming than other intervention options. The surgeon removes layers of skin one by one and examines them under a microscope. This process continues until the edges of the affected area are clear of cancerous elements.
Mohs surgery has become a cutting-edge treatment for skin cancer overseas, with success rates of around 99%.
Foreign oncologists use extensive surgical procedures in cases of advanced skin cancer.
Wide local excision
The surgery involves removing the cancerous tissue and a margin of surrounding healthy skin. This method is used to treat melanoma, basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma.
Skin transplantation
If surgery removes most of the cancerous skin, the surgeon may use a skin flap or graft to reconstruct the operated area. Donor skin is taken from another part of the body – the thigh or groin. When using skin flaps, the surgeon reconstructs the surgical field with tissue of a similar color and texture.
The advantage of skin grafts is that the tissue removed has its own blood supply. Flaps can be used when the skinless area has poor blood supply due to damaged blood vessels. In the head and neck area, flaps of adjacent tissue can improve the cosmetic effect.
Before surgery for skin cancer, the oncologist checks the lymph nodes that are located near the tumor. For this, the patient undergoes computed tomography, PET-CT, and ultrasound. These studies can detect metastases up to 0.2 mm.
If the doctor confirms the presence of cancer cells in the regional lymph nodes, the patient will need additional surgery to remove them. Lymph nodes act as filters that can trap and transport tumor cells throughout the body. Therefore, in some cases, it is necessary to perform lymphadenectomy.
Removal of lymph nodes can be performed by an oncologist or a highly specialized specialist – a head and neck surgeon.

According to reviews about melanoma treatment abroad, Experts Medical specialists can highlight the following advantages:
- access to advanced therapies;
- achieving long-term remission by patients even in complex cases of skin cancer;
- a combination of advanced treatment methods helps to avoid relapse even in older people.
Based on the results of melanoma treatment abroad, in reviews, patients often note rapid diagnosis (on average 1-2 days).
Skin cancer treatment abroad takes place in a friendly environment. Patients pay for all medical services only through the clinic’s cash desk.
Which clinics do foreigners most often choose? According to the number of requests to Experts Medical, patients prefer to carry out skin cancer treatment abroad in the Turkish multidisciplinary centers Memorial and Acibadem, as well as in the German hospital Helios Krefeld. These clinics employ experienced specialists in the treatment of skin cancer and reconstructive surgery.
Leave a request on the Experts Medical website to go abroad for skin cancer treatment. The coordinating doctor will help you choose a suitable medical center and specialized oncologist.
Why should you entrust the process of organizing a trip for skin cancer treatment abroad to Experts Medical? The international company cooperates with accredited and verified clinics. Among them, there are public and private hospitals. The cost of treatment will differ, so the patient’s choice is often related to pricing.
Some medical centers offer attractive package deals that may include:
- airport transfer;
- initial consultation with an oncologist;
- histological analysis;
- blood tests;
- surgery;
- rehabilitation course.
Coordinating doctors will be able to choose the best option for you based on reviews from patients who have already undergone successful treatment for skin cancer abroad.









